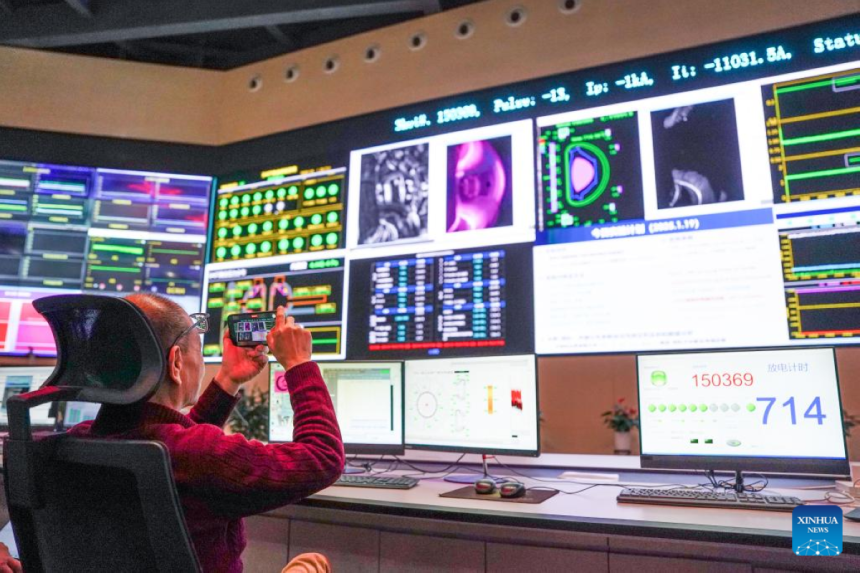
Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak
China has achieved a significant milestone in nuclear energy with a new nuclear fusion experiment.
The Chinese “Artificial Sun” reactor, known as EAST (Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak), maintained plasma for 1,000 seconds.
Surpassing the previous record of 403 seconds set in 2023.
During this experiment, the reactor reached an astonishing temperature of 100 million degrees Celsius.
Achieving high temperatures and sustaining reactor operation for extended periods is a significant challenge in nuclear fusion.
But scientists see this achievement as an important step toward improving the technology.

Achieving sustainability in plasma loops
Song Yuntao, Director of the Institute of Plasma Physics at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, said:
“The continuous efficient operation of the fusion device is essential for achieving sustainable power generation for future fusion plants.”
He added that China hopes to enhance international cooperation in this field and practically apply fusion energy to serve humanity.
Although the reactor has not yet reached the “ignition” stage, where nuclear fusion releases its own energy, this new record is a positive indicator towards achieving sustainability in plasma loops, which are crucial for operating future reactors.
Since the Chinese Artificial Sun initial operation in 2006, Chinese scientists have conducted numerous tests.
As a result of this success, China has begun building new facilities for nuclear fusion research in Anhui Province.
In order to accelerate the development and application of fusion energy.
The UAE Pavilion at the 55th Annual Meeting of the World Economic Forum (WEF) hosted a panel discussion titled “Global Competitiveness in a Changing World,” in which His Excellency Abdullah bin Touq Al Marri, Minister of Economy, addressed the rapid transformations that are… pic.twitter.com/0lQOS71DqU
— UAE Voice (@uae_voiceeng) January 22, 2025
The Chinese Artificial Sun: A Solution For Global Energy Problem
Scientists consider nuclear fusion a promising solution to the global energy problem.
As it relies on the same process that powers the sun.
It differs from nuclear fission in that it does not produce greenhouse gases.
It also doesn’t pose any significant risk to the environment or humans.
This makes it a source of sustainable energy that can help address the current energy crisis and support space exploration.
Notably, China is a key member of the ITER collaboration along with the European Union, India, Japan, Russia, South Korea, and the United States.
With the ITER reactor expected to begin its first experiments in 2034.