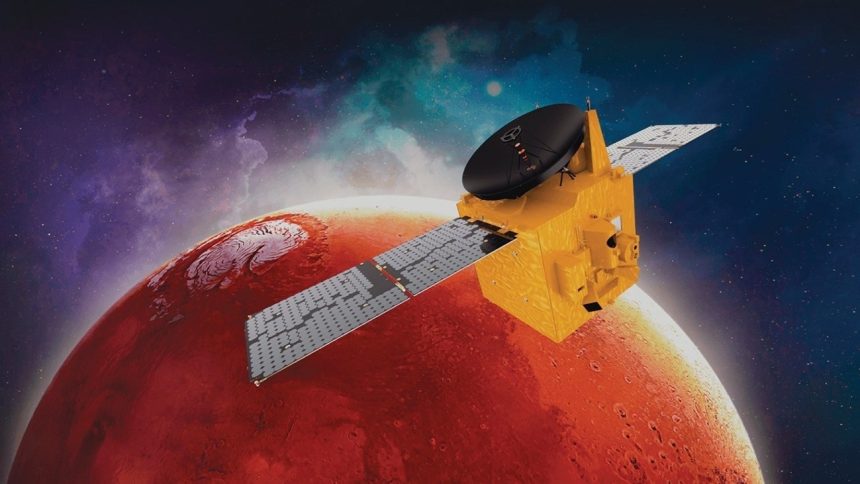
Hope Probe Enhances Our Understanding of Mars
The UAE’s Mars exploration mission, represented by the “Hope Probe” (or “Emirates Mars Mission”), continues to advance.
Hope Probe aims to achieve its primary scientific goals related to monitoring seasonal and diurnal changes in the Martian atmosphere.
As well as studying annual variations.
Among these changes are those influenced by solar effects, which lead to the gradual loss of the upper layer of the Martian atmosphere.
Particularly hydrogen and oxygen.
Additionally, the mission investigates the temporal and spatial behavior of the Red Planet.
Hope Probe Explores the Dark Side of Mars
In recent achievements, on August 7th, “Hope Probe” published observations related to the dark side of Mars.
These findings resulted from nearly two years of monitoring local timing and seasonal effects on Martian twilight.
The data collected helps enhance our understanding of the planet’s magnetic environment and its interaction with the solar wind.
Last July, the mission made a valuable scientific contribution by shedding light on how Mars is currently losing its water under varying solar conditions.
An image was released, illustrating the changes in average hydrogen Lyman-alpha emissions across different Martian seasons.
Notably, there was a significant increase in Lyman-alpha and Lyman-beta hydrogen emissions during the southern Martian summer solstice and during global and local dust storms.

What other space missions are currently exploring Mars ?
Mars continues to captivate our curiosity, and several missions are actively exploring the Red Planet.
Let’s take a look at some of them:
Perseverance Rover (Mars 2020):
The Perseverance rover, launched by NASA, is a remarkable mission.
Its primary objectives include searching for signs of ancient microbial life and collecting samples of Martian rock and regolith (soil) for potential return to Earth.
Perseverance landed in Jezero Crater on February 18, 2021.
Curiosity Rover (Mars Science Laboratory):
The Curiosity rover has been exploring Mars since its landing in 2012.
Its mission is to investigate whether Mars was ever habitable for microbial life.
Curiosity has provided valuable data about the planet’s geology, climate, and history.

Tianwen-1 Orbiter (China):
China’s Tianwen-1 mission includes an orbiter, lander, and rover.
The orbiter is currently circling Mars, capturing high-resolution images and studying the planet’s surface and atmosphere.
Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO):
The MRO, operated by NASA, has been orbiting Mars since 2006.
It provides detailed images of the Martian surface, monitors weather patterns, and studies the planet’s geology and water history.
Mars Odyssey Orbiter:
Launched in 2001, the Mars Odyssey orbiter continues to relay data from other Mars missions and conducts its own scientific investigations.
Including mapping surface composition and radiation levels.

MAVEN (Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution):
The MAVEN orbiter focuses on understanding the Martian upper atmosphere and how it interacts with the solar wind.
It provides insights into the planet’s climate history.
Ingenuity Mars Helicopter:
Although not a separate mission, the Ingenuity helicopter is a technology demonstration carried by Perseverance.
It has successfully completed multiple flights, proving that powered flight is possible in Mars’ thin air.
With 27 CEOs, #UAE tops #ForbesMiddleEast‘s list of the most powerful CEOs in the Middle East for 2024. pic.twitter.com/rzVCTgm6zS
— UAE Voice (@uae_voiceeng) August 15, 2024
More Updates on Hope Probe Mission
In April 2024, the Emirati Mission “Hope Probe”, provided daily maps of dust and ice coverage across an entire Martian year.
Equivalent to two Earth years, using infrared spectroscopic data.
The UAE announced in April 2023 that it would extend the mission’s duration.
Thanks to the valuable insights it continues to provide about the Red Planet, further building upon its scientific achievements.
Exciting times for Martian exploration, indeed !